- info@paca-environnement.com
- 1 rue du Gabian – Le Thalès 98000 Monaco
Rainwater management

Do you have a question?
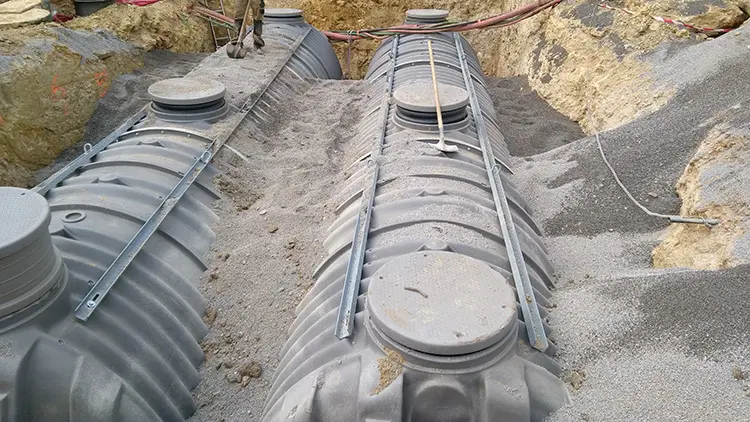

Rainwater management
Let water penetrate the soil by implementing so-called alternative techniques: retention basins, rain gardens, infiltration swales, draining trenches, etc. Many municipalities require water retention solutions when issuing building permits.
Current techniques make it possible to respond to these issues at a cost that is all the more reasonable if it can be treated at the same time as a non-collective sanitation project.
Rainwater management refers to the process of collecting, treating and distributing precipitation that falls as rain or snow. This management is essential to avoid flooding, minimize water pollution and optimize the use of water resources.
Here are the main steps and components of stormwater management:
1. Rainwater collection:
Collecting rainwater from impervious surfaces such as roofs, roads, parking lots, etc.
Using drainage systems such as gutters, downspouts, storm sewers and canals to direct water to collection points.
2. Storage and retention:
Temporary storage of rainwater in retention basins, regulation ponds or reservoirs.
This step helps reduce the flow of rainwater which quickly reaches drainage systems and watercourses, thus minimizing the risk of flooding.
3. Rainwater treatment:
Treatment may be necessary to remove contaminants such as chemical pollutants, sediment and heavy metals from rainwater.
Treatment techniques include filtration, biological remediation, sediment separation, and other methods to improve water quality.
4. Distribution of rainwater:
Treated rainwater can be reused for non-potable purposes, such as irrigation, vehicle washing, flushing toilets, etc., thereby reducing the demand for potable water.
Rainwater can also be discharged into waterways if it meets water quality standards.
5. Sustainable management:
Rainwater management practices are evolving towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly approaches, such as the development of permeable surfaces, the revegetation of roofs (green roofs), and the creation of artificial wetlands.
These approaches reduce the impact of rainwater on the environment by promoting natural infiltration and limiting runoff.
6. Planning and regulation:
Local authorities often develop stormwater management plans to guide development and land use planning practices.
Specific regulations can be put in place to ensure that new construction incorporates adequate stormwater management systems.
In summary, rainwater management aims to minimize flood risks, preserve water quality, optimize the use of water resources and promote more sustainable water management practices. It is crucial for environmental protection and efficient management of water resources. The government has recently introduced aid for the installation of rainwater management systems, our customer service representatives will guide you in allowing you to benefit from this aid.
Rainwater management
Our range

KIT DE RECUPERATION
EAU DE PLUIE
Ce kit contient une cuve et une pompe. Il sera connecté à la fois à vos gouttières et votre réseau d’eau de ville. Cela permettra d’avoir toujours le niveau adéquat dans la cuve.
Capacité : 2000 à 8000 litres.


CITERNEO
CITERNE SOUPLE
Cette citerne souple peut-être installée en vide sanitaire, sous une terrasse, ou même au fond de votre jardin et constituera une réserve d’eau de pluie pour arroser vos plantes.
Capacité : 1000 à 50 000 litres.


DEBOURBEUR
ET SEPARATEUR HYDRO
Ce système est installé habituellement sur des aires de stationnement afin de recueillir et de séparer l’eau pluviale et les hydrocarbures.
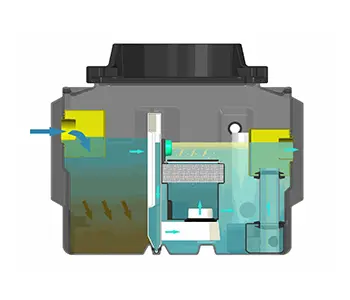

MILLENIUM
PREMIER TECH
La cuve millénium permet la récupération de vos eaux pluviales. Capacité : 5000 et 6000 litres.


